Rickets
Osteomalacia in children; Vitamin D deficiency; Renal rickets; Hepatic rickets
Rickets is a disorder caused by a lack of vitamin D, calcium, or phosphate. It leads to softening and weakening of the bones.
Causes
Vitamin D helps the body control calcium and phosphate levels. If the blood levels of these minerals become too low, the body may produce hormones that cause calcium and phosphate to be released from the bones. This leads to weak and soft bones.
Vitamin D
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin. Fat-soluble vitamins are stored in the body's fatty tissue.

Vitamin D is absorbed from food or produced by the skin when exposed to sunlight. Lack of vitamin D production by the skin may occur in people who:
- Live in climates with little exposure to sunlight
- Must stay indoors
- Work indoors during the daylight hours
You may not get enough vitamin D from your diet if you:
-
Are
lactose intolerant
(have trouble digesting milk products)
Lactose intolerant
Lactose is a type of sugar found in milk and other dairy products. An enzyme called lactase is needed by the body to digest lactose. Lactose intoler...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - DO NOT drink milk products
- Follow a vegetarian diet
Infants who are breastfed only may develop vitamin D deficiency. Human breast milk does not supply the proper amount of vitamin D. This can be a particular problem for darker-skinned children in winter months. This is because there are lower levels of sunlight during these months.
Not getting enough calcium and phosphorous in your diet can also lead to rickets. Rickets caused by a lack of these minerals in diet is rare in developed countries. Calcium and phosphorous are found in milk and green vegetables.
Your genes may increase your risk of rickets. Hereditary rickets is a form of the disease that is passed down through families. It occurs when the kidneys are unable to hold onto the mineral phosphate. Rickets may also be caused by kidney disorders that involve renal tubular acidosis .
Renal tubular acidosis
Proximal renal tubular acidosis is a disease that occurs when the kidneys don't properly remove acids from the blood into the urine. As a result, to...

Disorders that reduce the digestion or absorption of fats will make it more difficult for vitamin D to be absorbed into the body.
Sometimes, rickets may occur in children who have disorders of the liver. These children cannot convert vitamin D to its active form.
Rickets is rare in the United States. It is most likely to occur in children during periods of rapid growth. This is the age when the body needs high levels of calcium and phosphate. Rickets may be seen in children ages 6 to 24 months. It is uncommon in newborns.
Symptoms
Symptoms of rickets include:
-
Bone pain or tenderness
in the arms, legs, pelvis, and spine
Bone pain or tenderness
Bone pain or tenderness is aching or other discomfort in one or more bones.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Decreased muscle tone
(loss of muscle strength) and
weakness
that gets worse
Decreased muscle tone
Hypotonia means decreased muscle tone.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Dental deformities, including delayed tooth formation, defects in the tooth structure, holes in the enamel, and increased cavities (
dental caries
)
Dental caries
Dental cavities are holes (or structural damage) in the teeth.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Impaired growth
Impaired growth
Delayed growth is poor or abnormally slow height or weight gains in a child younger than age 5. This may just be normal, and the child may outgrow i...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Increased bone fractures
-
Muscle cramps
Muscle cramps
Muscle cramps are when a muscle gets tight (contracts) without you trying to tighten it, and it does not relax. Cramps may involve all or part of on...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Short stature
(adults less than 5 feet or 1.52 meters tall)
Short stature
A child who has short stature is much shorter than children who are the same age and sex. Your health care provider will go over your child's growth ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Skeletal deformities
such as an odd-shaped skull,
bowlegs
, bumps in the ribcage (rachitic rosary), breastbone that is pushed forward (pigeon chest), pelvic deformities, and spine deformities (spine that curves abnormally, including
scoliosis
or
kyphosis
)
Skeletal deformities
Skeletal limb abnormalities refers to a variety of bone structure problems in the arms or legs (limbs).
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleBowlegs
Bowlegs is a condition in which the knees stay wide apart when a person stands with the feet and ankles together. It is considered normal in childre...
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleScoliosis
Scoliosis is an abnormal curving of the spine. Your spine is your backbone. It runs straight down your back. Everyone's spine naturally curves a b...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleKyphosis
Kyphosis is a curving of the spine that causes a bowing or rounding of the back. This leads to a hunchback or slouching posture.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Exams and Tests
A physical exam reveals tenderness or pain in the bones, but not in the joints or muscles.
The following tests may help diagnose rickets:
-
Arterial blood gases
Arterial blood gases
Blood gases are a measurement of how much oxygen and carbon dioxide are in your blood. They also determine the acidity (pH) of your blood.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Blood tests (
serum calcium
)
Serum calcium
The calcium blood test measures the level of calcium in the blood. This article discusses the test to measure the total amount of calcium in your blo...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Bone biopsy
(rarely done)
Bone biopsy
A bone lesion biopsy is the removal of a piece of bone or bone marrow for examination.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Bone x-rays
Bone x-rays
A bone x-ray is an imaging test to look at the bones.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Serum alkaline phosphatase
(ALP)
Serum alkaline phosphatase
Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) is a protein found in all body tissues. Tissues with higher amounts of ALP include the liver, bile ducts, and bone. A blo...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Serum phosphorus
Serum phosphorus
The phosphorus blood test measures the amount of phosphate in the blood.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Other tests and procedures include the following:
-
ALP isoenzyme
ALP isoenzyme
Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) is an enzyme found in many body tissues such as liver, bile ducts, bone, and intestine. There are several different forms...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Calcium (ionized)
Calcium (ionized)
Ionized calcium is calcium in your blood that is not attached to proteins. It is also called free calcium. All cells need calcium in order to work. ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Parathyroid hormone (
PTH
)
PTH
The PTH test measures the level of parathyroid hormone in the blood. PTH stands for parathyroid hormone. It is a protein hormone released by the par...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Urine calcium
Urine calcium
This test measures the amount of calcium in urine. All cells need calcium in order to work. Calcium helps build strong bones and teeth. It is impo...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
The goals of treatment are to relieve symptoms and correct the cause of the condition. The cause must be treated to prevent the disease from returning.
Replacing calcium, phosphorus, or vitamin D that is lacking will eliminate most symptoms of rickets. Dietary sources of vitamin D include fish liver and processed milk.
Exposure to moderate amounts of sunlight is encouraged. If rickets is caused by a metabolic problem, a prescription for vitamin D supplements may be needed.
Positioning or bracing may be used to reduce or prevent deformities. Some skeletal deformities may require surgery to correct them.
Outlook (Prognosis)
The disorder may be corrected by replacing vitamin D and minerals. Laboratory values and x-rays usually improve after about 1 week. Some cases may require large doses of minerals and vitamin D.
If rickets is not corrected while the child is still growing, skeletal deformities and short stature may be permanent. If it is corrected while the child is young, skeletal deformities often improve or disappear with time.
Possible Complications
Possible complications are:
-
Long-term (
chronic
) skeletal pain
Chronic
Chronic refers to something that continues over an extended period of time. A chronic condition is usually long-lasting and does not easily or quick...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Skeletal deformities
- Skeletal fractures, may occur without cause
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call your child's health care provider if you notice symptoms of rickets.
Prevention
You can prevent rickets by making sure that your child gets enough calcium, phosphorus, and vitamin D in the diet. Children who have digestive or other disorders may need to take supplements the child’s provider prescribed.
Kidney (renal) diseases, that may cause poor vitamin D absorption, should be treated right away. If you have renal disorders , monitor calcium and phosphorus levels regularly.
Renal disorders
A renal disorder refers to any disease of the kidneys. Urological disorders are diseases of the kidneys and urinary tract. This includes the kidneys...

Genetic counseling may help people who have a family history of inherited disorders that can cause rickets.
References
Greenbaum LA. Rickets and hypervitaminosis D. In: Kliegman RM, Stanton BF, St. Geme JW, Schor NF, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics . 20th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2016:chap 51.
Whiting SJ, Calvo MS. Nutrition and lifestyle effects on vitamin D status. In: Feldman D, Pike JW, Adams JS, eds. Vitamin D . 3rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2011:chap 54.
-
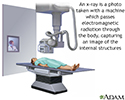
X-ray - illustration
X-rays are a form of ionizing radiation that can penetrate the body to form an image on film. Structures that are dense (such as bone) will appear white, air will be black, and other structures will be shades of gray depending on density. X-rays can provide information about obstructions, tumors, and other diseases, especially when coupled with the use of barium and air contrast within the bowel.
X-ray
illustration
-
X-ray - illustration
X-rays are a form of ionizing radiation that can penetrate the body to form an image on film. Structures that are dense (such as bone) will appear white, air will be black, and other structures will be shades of gray depending on density. X-rays can provide information about obstructions, tumors, and other diseases, especially when coupled with the use of barium and air contrast within the bowel.
X-ray
illustration
Review Date: 8/31/2016
Reviewed By: Neil K. Kaneshiro, MD, MHA, Clinical Assistant Professor of Pediatrics, University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.