Hot tub folliculitis
Hot tub folliculitis is an infection of the skin around the lower part of the hair shaft (hair follicles). It occurs when you come into contact with certain bacteria that live in warm and wet areas.
Folliculitis
Folliculitis is inflammation of one or more hair follicles. It can occur anywhere on the skin.

Causes
Hot tub folliculitis is caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa , a bacteria that survives in hot tubs, especially tubs made of wood.
Symptoms
The first symptom of hot tub folliculitis is an itchy, bumpy, and red rash. Symptoms can appear from several hours to 2 days after contact with the bacteria.
The rash may:
Rash
Rashes involve changes in the color, feeling or texture of your skin.

-
Turn into dark red tender
nodules
Nodules
Skin nodules are solid or cystic raised bumps in the skin that are wider than 1 centimeter (cm), but less than 2 cm.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Have bumps that fill with pus
- Look like acne
- Be thicker under swimsuit areas where the water was in contact with the skin for longer
Other people who used the hot tub may have the same rash.
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider can often make this diagnosis based on looking at the rash and knowing that you have been in a hot tub. Testing is usually not needed.
Treatment
Treatment may not be needed. The mild form of the disease often clears on its own. Anti-itch medicines may be used to ease discomfort.
In severe cases, your provider may prescribe an antibiotic.
Outlook (Prognosis)
This condition usually clears without scarring. The problem may come back if you use the hot tub again before it has been cleaned.
Possible Complications
In rare cases, a collection of pus ( abscess ) may form.
Abscess
An abscess is a collection of pus in any part of the body. In most cases, the area around an abscess is swollen and inflamed.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call your health care provider if you develop symptoms of hot tub folliculitis.
Prevention
Controlling the acid levels and chlorine content of the hot tub may help prevent the problem.
References
D'Agata E. Pseudomonas aeruginosa and other Pseudomonas species. In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases, Updated Edition . 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2015:chap 221.
Lacuesta MPM, Phelps RG. Folliculitis. In: Lebwohl MG, Heymann WR, Berth-Jones J, Coulson I, eds. Treatment of Skin Disease: Comprehensive Therapeutic Strategies . 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2014:chap 83.
-
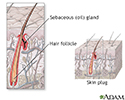
Hair follicle anatomy - illustration
At the base of the hair follicle are sensory nerve fibers that wrap around each hair bulb. Bending the hair stimulates the nerve endings allowing a person to feel that the hair has been moved. One of the main functions of hair is to act as a sensitive touch receptor. Sebaceous glands are also associated with each hair follicle that produce an oily secretion to help condition the hair and surrounding skin.
Hair follicle anatomy
illustration
-
Hair follicle anatomy - illustration
At the base of the hair follicle are sensory nerve fibers that wrap around each hair bulb. Bending the hair stimulates the nerve endings allowing a person to feel that the hair has been moved. One of the main functions of hair is to act as a sensitive touch receptor. Sebaceous glands are also associated with each hair follicle that produce an oily secretion to help condition the hair and surrounding skin.
Hair follicle anatomy
illustration
Review Date: 10/24/2016
Reviewed By: David L. Swanson, MD, Vice Chair of Medical Dermatology, Associate Professor of Dermatology, Mayo Medical School, Scottsdale, AZ. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.