Dermatoses - systemic
Dermatoses is a general term used to describe any skin defect or lesion on the skin. Systemic means it affects the whole body, rather than just one part. Systemic dermatoses may be linked to problems in other organs.
Systemic
Systemic means affecting the entire body, rather than a single organ or body part. For example, systemic disorders, such as high blood pressure, or s...
Examples include:
- Psoriasis
- Dermatomyositis
- Polyangiitis
- Systemic lupus erythematosus
- Erythema nodosum
References
Lee LA, Werth VP. The skin and ryheumatic diseases. In: Firestein GS, Budd RC, Harris ED Jr, et al, eds. Kelley's Textbook of Rheumatology . 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2012:chap 43.
-
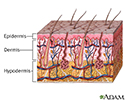
Skin layers - illustration
The skin is the largest organ of the body. The skin and its derivatives (hair, nails, sweat and oil glands) make up the integumentary system. One of the main functions of the skin is protection. It protects the body from external factors such as bacteria, chemicals, and temperature. The skin contains secretions that can kill bacteria and the pigment melanin provides a chemical pigment defense against ultraviolet light that can damage skin cells. Another important function of the skin is body temperature regulation. When the skin is exposed to a cold temperature, the blood vessels in the dermis constrict. This allows the blood which is warm, to bypass the skin. The skin then becomes the temperature of the cold it is exposed to. Body heat is conserved since the blood vessels are not diverting heat to the skin anymore. Among its many functions the skin is an incredible organ always protecting the body from external agents.
Skin layers
illustration
-
Skin layers - illustration
The skin is the largest organ of the body. The skin and its derivatives (hair, nails, sweat and oil glands) make up the integumentary system. One of the main functions of the skin is protection. It protects the body from external factors such as bacteria, chemicals, and temperature. The skin contains secretions that can kill bacteria and the pigment melanin provides a chemical pigment defense against ultraviolet light that can damage skin cells. Another important function of the skin is body temperature regulation. When the skin is exposed to a cold temperature, the blood vessels in the dermis constrict. This allows the blood which is warm, to bypass the skin. The skin then becomes the temperature of the cold it is exposed to. Body heat is conserved since the blood vessels are not diverting heat to the skin anymore. Among its many functions the skin is an incredible organ always protecting the body from external agents.
Skin layers
illustration
Review Date: 1/13/2015
Reviewed By: Jacob L. Heller, MD, MHA, emergency medicine, Virginia Mason Medical Center, Seattle, Washington. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.