Autosomal dominant
Inheritance - autosomal dominant; Genetics - autosomal dominant
Autosomal dominant is one of several ways that a trait or disorder can be passed down (inherited) through families.
In an autosomal dominant disease, if you inherit the abnormal gene from only one parent, you can get the disease. Often, one of the parents may also have the disease.
Gene
A gene is a short piece of DNA. Genes tell the body how to build specific proteins. There are about 20,000 genes in each cell of the human body. T...
Information
Inheriting a disease, condition, or trait depends on the type of chromosome affected (nonsex or sex chromosome ). It also depends on whether the trait is dominant or recessive.
Sex chromosome
Sex-linked dominant is a rare way that a trait or disorder can be passed down through families. One abnormal gene on the X chromosome can cause a se...

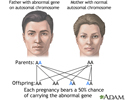
A single abnormal gene on one of the first 22 nonsex ( autosomal ) chromosomes from either parent can cause an autosomal disorder.
Autosomal
Chromosomes are structures found in the center (nucleus) of cells that carry long pieces of DNA. DNA is the material that holds genes. It is the bu...

Dominant inheritance means an abnormal gene from one parent can cause disease. This happens even when the matching gene from the other parent is normal. The abnormal gene dominates.
This disease can also occur as a new condition in a child when neither parent has the abnormal gene.
A parent with an autosomal dominant condition has a 50% chance of having a child with the condition. This is true for each pregnancy.
It means that each child's risk for the disease does not depend on whether their sibling has the disease.
Children who do not inherit the abnormal gene will not develop or pass on the disease.
If someone is diagnosed with an autosomal dominant disease, their parents should also be tested for the abnormal gene.
Examples of autosomal dominant disorders include
Huntington disease
and
neurofibromatosis type 1
.
Huntington disease
Huntington disease is a disorder in which nerve cells in certain parts of the brain waste away, or degenerate. The disease is passed down through fa...
Neurofibromatosis type 1
Neurofibromatosis-1 (NF1) is an inherited disorder in which nerve tissue tumors (neurofibromas) form in the: Bottom layer of skin (subcutaneous tissu...

References
Scott DA, Lee B. Patterns of genetic transmission. In: Kliegman RM, Stanton BF, St Geme JW, Schor NF, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 20th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2016:chap 80.
Wiggs JL. Fundamentals of human genetics. In: Yanoff M, Duker JS, eds.
Ophthalmology.
4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2014:chap 1.1.
-
Autosomal dominant genes - illustration
In the case of autosomal dominant genes, a single abnormal gene on one of the autosomal chromosomes (one of the first 22 "non-sex" chromosomes) from either parent can cause the disease. One of the parents will have the disease (since it is dominant) in this mode of inheritance and that person is called the CARRIER. Only one parent must be a carrier in order for the child to inherit the disease.
Autosomal dominant genes
illustration
-
Autosomal dominant genes - illustration
In the case of autosomal dominant genes, a single abnormal gene on one of the autosomal chromosomes (one of the first 22 "non-sex" chromosomes) from either parent can cause the disease. One of the parents will have the disease (since it is dominant) in this mode of inheritance and that person is called the CARRIER. Only one parent must be a carrier in order for the child to inherit the disease.
Autosomal dominant genes
illustration
Review Date: 2/15/2016
Reviewed By: Neil K. Kaneshiro, MD, MHA, Clinical Assistant Professor of Pediatrics, University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.