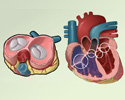
Pulmonary valve stenosis
Valvular pulmonary stenosis; Heart valve pulmonary stenosis; Pulmonary stenosis; Stenosis - pulmonary valve; Balloon valvuloplasty - pulmonary
Pulmonary valve stenosis is a heart valve disorder that involves the pulmonary valve.
This is the valve separating the right ventricle (one of the chambers in the heart) and the pulmonary artery. The pulmonary artery carries oxygen-poor blood to the lungs.
Stenosis, or narrowing, occurs when the valve cannot open wide enough. As a result, less blood flows to the lungs.
Causes
Narrowing of the pulmonary valve is most often present at birth (congenital). It is caused by a problem that occurs as the baby develops in the womb before birth. The cause is unknown, but genes may play a role.
Narrowing that occurs in the valve itself is called pulmonary valve stenosis. There may also be narrowing just before or after the valve.
The defect may occur alone or with other heart defects that are present at birth. The condition can be mild or severe.
Pulmonary valve stenosis is a rare disorder. In some cases, the problem runs in families.
Symptoms
Many cases of pulmonary valve stenosis are mild and do not cause symptoms. The problem is most often found in infants when a heart murmur is heard during a routine heart exam.
When the valve narrowing (stenosis) is moderate to severe, the symptoms include:
-
Abdominal distention
Abdominal distention
A swollen abdomen is when your belly area is bigger than usual.
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Bluish color to the skin
(cyanosis) in some people
Bluish color to the skin
Cyanosis is a bluish color to the skin or mucous membrane that is usually due to a lack of oxygen in the blood.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Poor appetite
-
Chest pain
Chest pain
Chest pain is discomfort or pain that you feel anywhere along the front of your body between your neck and upper abdomen.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Fainting
Fainting
Fainting is a brief loss of consciousness due to a drop in blood flow to the brain. The episode most often lasts less than a couple of minutes and y...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Fatigue
Fatigue
Fatigue is a feeling of weariness, tiredness, or lack of energy.
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Poor weight gain or
failure to thrive
in infants with a severe blockage
Failure to thrive
Failure to thrive refers to children whose current weight or rate of weight gain is much lower than that of other children of similar age and gender....
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Shortness of breath
Shortness of breath
Breathing difficulty may involve:Difficult breathingUncomfortable breathingFeeling like you are not getting enough air
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Sudden death
Symptoms may get worse with exercise or activity.
Exams and Tests
The health care provider may hear a heart murmur when listening to the heart using a stethoscope. Murmurs are blowing, whooshing, or rasping sounds heard during a heartbeat.
Heart murmur
A heart murmur is a blowing, whooshing, or rasping sound heard during a heartbeat. The sound is caused by turbulent (rough) blood flow through the h...

Tests used to diagnose pulmonary stenosis may include:
-
Cardiac catheterization
Cardiac catheterization
Cardiac catheterization involves passing a thin flexible tube (catheter) into the right or left side of the heart. The catheter is most often insert...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Chest x-ray
-
ECG
ECG
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a test that records the electrical activity of the heart.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Echocardiogram
Echocardiogram
An echocardiogram is a test that uses sound waves to create pictures of the heart. The picture and information it produces is more detailed than a s...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
MRI of the heart
MRI of the heart
Heart magnetic resonance imaging is an imaging method that uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create pictures of the heart. It does not use ra...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
The provider will grade the severity of the valve stenosis to plan treatment.
Treatment
Sometimes, treatment may not be needed if the disorder is mild.
When there are also other heart defects, medicines may be used to:
- Help blood flow through the heart (prostaglandins)
- Help the heart beat stronger
- Prevent clots (blood thinners)
- Remove excess fluid (water pills)
- Treat abnormal heartbeats and rhythms
Percutaneous balloon pulmonary dilation (valvuloplasty) may be performed when no other heart defects are present.
- This procedure is done through an artery in the groin.
- The doctor sends a flexible tube (catheter) with a balloon attached to the end up to the heart. Special x-rays are used to help guide the catheter.
- The balloon stretches the opening of the valve.
Some people may need heart surgery to repair or replace the pulmonary valve. The new valve can be made from different materials. If the valve cannot be repaired or replaced, other procedures may be needed.
Outlook (Prognosis)
People with mild disease rarely get worse. However, those with moderate to severe disease will get worse. The outcome is often very good when surgery or balloon dilation is successful. Other congenital heart defects may be a factor in the outlook.
Most often, the new valves can last for decades. However, some will wear out and need to be replaced.
Possible Complications
Complications may include:
-
Abnormal heartbeats (
arrhythmias
)
Arrhythmias
An arrhythmia is a disorder of the heart rate (pulse) or heart rhythm. The heart can beat too fast (tachycardia), too slow (bradycardia), or irregul...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Death
-
Heart failure
and enlargement of the right side of the heart
Heart failure
Heart failure is a condition in which the heart is no longer able to pump oxygen-rich blood to the rest of the body efficiently. This causes symptom...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Leaking of blood back into the right ventricle (pulmonary regurgitation) after repair
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call your provider if:
- You have symptoms of pulmonary valve stenosis.
- You have been treated or have untreated pulmonary valve stenosis and have developed swelling (of the ankles, legs, or abdomen), difficulty breathing, or other new symptoms.
References
Carabello BA. Valvular heart disease. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman's Cecil Medicine . 25th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2016:chap 75.
Marelli AJ. Congenital heart disease in adults. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman's Cecil Medicine . 25th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2016:chap 69.
Otto CM, Bownow RO. Valvular heart disease. In: Mann DL, Zipes DP, Libby P, Bonow RO, Braunwald E, eds. Braunwald's Heart Disease: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine . 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2015:chap 63.
Webb GD, Smallhorn JF, Therrien J, Redington AN. Congenital heart disease. In: Mann DL, Zipes DP, Libby P, Bonow RO, Braunwald E, eds. Braunwald's Heart Disease: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine . 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2015:chap 62.
-
Valvular heart disease (VHD) overview
Animation
-
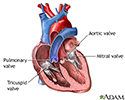
Heart valves - illustration
The valves of the heart open and close to control the flow of blood entering or leaving the heart.
Heart valves
illustration
Review Date: 5/24/2016
Reviewed By: Mary C. Mancini, MD, PhD, Department of Surgery, Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center-Shreveport, Shreveport, LA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.