Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is irritation and swelling (inflammation) of the liver due to infection with the hepatitis B virus (HBV).
Other types of viral hepatitis include hepatitis A , hepatitis C , and hepatitis D .
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A is inflammation (irritation and swelling) of the liver from the hepatitis A virus.

Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is a viral disease that leads to swelling (inflammation) of the liver. Other types of viral hepatitis include:Hepatitis AHepatitis BHepat...

Hepatitis D
Hepatitis D is a viral infection caused by the hepatitis D virus (previously called the Delta agent). It causes symptoms only in people who also hav...

Causes
Hepatitis B infection is caused by the HBV. You can catch hepatitis B through contact with the blood or body fluids (semen, vaginal fluids, and saliva) of a person who has the virus.
Exposure may occur:
- After a needlestick or sharps injury
- If any blood or other body fluid touches your skin, eyes or mouth, or open sores or cuts
People who may be at risk of hepatitis B are those who:
- Have unprotected sex with an infected partner
- Receive blood transfusions (not common in the United States)
- Have contact with blood at work (such as health care workers)
- Have been on long-term kidney dialysis
- Get a tattoo or acupuncture with unclean needles
- Share needles during drug use
- Share personal items (such as toothbrush, razor, and nail clippers) with a person who has the virus
- Were born to a hepatitis-B infected mother
All blood used for blood transfusions is screened, so the chance of getting the virus in this way is very small.
Symptoms
After you first become infected with the HBV:
- You may have no symptoms.
- You may feel sick for a period of days or weeks.
- You may become very ill very quickly (called fulminant hepatitis).
Symptoms of hepatitis B may not appear for up to 6 months after the time of infection. Early symptoms include:
- Appetite loss
- Fatigue
- Low fever
- Muscle and joint aches
- Nausea and vomiting
- Yellow skin and dark urine
Symptoms will go away in a few weeks to months if your body is able to fight off the infection. Some people never get rid of the HBV. This is called chronic hepatitis B.
People with chronic hepatitis may not have symptoms and not know they are infected. Over time, they may develop symptoms of liver damage and cirrhosis of the liver.
Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis is scarring of the liver and poor liver function. It is the last stage of chronic liver disease.

You can spread the HBV to other people even if you have no symptoms.
Exams and Tests
A series of blood tests called the hepatitis viral panel is done for suspected hepatitis. It can help detect:
Hepatitis viral panel
The hepatitis virus panel is a series of blood tests used to detect current or past infection by hepatitis A, hepatitis B, or hepatitis C. It can sc...

- New infection
- Older infection that is still active
- Older infection that is no longer active
The following tests are done to look for liver damage if you have chronic hepatitis B:
-
Albumin level
Albumin level
Albumin is a protein made by the liver. A serum albumin test measures the amount of this protein in the clear liquid portion of the blood. Albumin c...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Liver function tests
Liver function tests
Liver function tests are common tests that are used to see how well the liver is working. Tests include:AlbuminAlpha-1 antitrypsin Alkaline phosph...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Prothrombin time
Prothrombin time
Prothrombin time (PT) is a blood test that measures the time it takes for the liquid portion (plasma) of your blood to clot. A related blood test is ...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article
You will also have a test to measure the level of HBV in your blood (viral load). This lets your health care provider know how your treatment is working.
People at higher risk for hepatitis should be screened with a blood test. This may be needed even when they have no symptoms. Factors that lead to increased risk include:
- The risk factors described above in the Causes section.
- People from countries where a higher number of people have hepatitis B. These countries or areas include Japan, some Mediterranean countries, parts of Asia and the Middle East, West Africa and South Sudan.
Treatment
Acute hepatitis, unless severe, needs no treatment. Liver and other body functions are watched using blood tests. You should get plenty of bed rest, drink plenty of fluids, and eat healthy foods.
Some people with chronic hepatitis may be treated with antiviral drugs. These medicines can decrease or remove hepatitis B from the blood. One of the medicines is an injection called interferon. They also help to reduce the risk of cirrhosis and liver cancer.
It is not always clear which people with chronic hepatitis B should receive drug therapy and when it should be started. You are more likely to receive these medicines if:
- Your liver function is quickly becoming worse.
- You develop symptoms of long-term liver damage.
- You have high levels of the HBV in your blood.
For these medicines to work best, you need to take them as instructed by your provider. Ask what side effects you can expect and what to do if you have them. Not everybody who needs to take these medicines responds well.
If you develop liver failure, you may be considered for a liver transplant . A liver transplant is the only cure in some cases of liver failure.
Liver transplant
Liver transplant is surgery to replace a diseased liver with a healthy liver.

Other steps you can take:
- Avoid alcohol.
- Check with your provider before taking any over-the-counter medicines or herbal supplements. This includes medicines such as acetaminophen, aspirin, or ibuprofen.
Severe liver damage, or cirrhosis , can be caused by hepatitis B.
Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis is scarring of the liver and poor liver function. It is the last stage of chronic liver disease.

Support Groups
Some people benefit from attending a liver disease support group .
Liver disease support group
The following organizations are good resources for information on liver disease:American Liver Foundation -- www. liverfoundation. orgChildren's Live...

Outlook (Prognosis)
The acute illness most often goes away after 2 to 3 weeks. The liver most often returns to normal within 4 to 6 months in most people.
Acute
Acute means sudden or severe. Acute symptoms appear, change, or worsen rapidly. It is the opposite of chronic.

Almost all newborns and about half of children who get hepatitis B develop the chronic condition. Very few adults who get the virus develop chronic hepatitis B.
About 1 in 100 people who get hepatitis B dies from the condition.
There is a much higher rate of liver cancer in people who have chronic hepatitis B.
Liver cancer
Hepatocellular carcinoma is cancer that starts in the liver.

When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call your provider if:
- You develop symptoms of hepatitis B.
- Hepatitis B symptoms do not go away in 2 to 3 weeks, or new symptoms develop.
-
You belong to a high-risk group for hepatitis B and have not had the
HBV vaccine
.
HBV vaccine
All content below is taken in its entirety from the CDC Hepatitis B Vaccine Information Statement (VIS): www. cdc. gov/vaccines/hcp/vis/vis-statement...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article
Prevention
Children and people at high risk for hepatitis B should get the hepatitis B vaccine .
Hepatitis B vaccine
All content below is taken in its entirety from the CDC Hepatitis B Vaccine Information Statement (VIS): www. cdc. gov/vaccines/hcp/vis/vis-statement...
- Babies should get a first dose of the hepatitis B vaccine at birth. They should have all 3 shots in the series by age 6 to 18 months.
- Children younger than age 19 who have not had the vaccine should get "catch-up" doses.
- Health care workers and those who live with someone who has hepatitis B should get the vaccine.
- Infants born to mothers who have acute hepatitis B or have had the infection in the past should get a special hepatitis B vaccine within 12 hours of birth.
The hepatitis B vaccine or a hepatitis B immune globulin (HBIG) shot may help prevent infection if you receive it within 24 hours of contact with the virus.
Measures to avoid contact with blood and body fluids can help prevent the spread of hepatitis B from person-to-person.
Measures to avoid contact with blood an...
Hepatitis B and hepatitis C infections cause irritation and swelling of the liver. You should take steps to prevent catching or spreading these viru...
References
Kim DK, Bridges CB, Harriman KH; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC); Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP); ACIP Adult Immunization Work Group. Advisory committee on immunization practices (ACIP) recommended immunization schedules for adults aged 19 years and older -- United States, 2015. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep . 2015;64(4):91-92. PMID: 25654609 www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25654609 .
LeFevre ML; US Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for hepatitis B virus infection in nonpregnant adolescents and adults: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. Ann Intern Med . 2014;161(1):58-66. PMID 24863637 www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24863637 .
Pawlotsky J-M. Chronic viral and autoimmune hepatitis. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman's Cecil Medicine . 25th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2016:chap 149.
Sorrell MF, Belongia EA, Costa J, et al. National Institutes of Health Consensus Development Conference Statement: Management of hepatitis B. Ann Intern Med . 2009;150:104-10. PMID: 19124811 www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19124811 .
Strikas RA, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC); Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP); ACIP Child/Adolescent Immunization Work Group. Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) Recommended Immunization Schedules for Persons Aged 0 through 18 years -- United States, 2015. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep . 2015;64(4):93-94. PMID: 25654610 www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25654610 .
Wells JT, Perrillo R. Hepatitis B. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease . 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2016:chap 79.
-
Hepatitis B
Animation
-
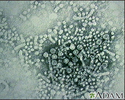
Hepatitis B virus - illustration
Hepatitis B is also known as serum hepatitis and is spread through blood and sexual contact. It is seen with increased frequency among intravenous drug users who share needles and among the homosexual population. This photograph is an electronmicroscopic image of hepatitis B virus particles. (Image courtesy of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.)
Hepatitis B virus
illustration
-
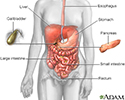
Digestive system - illustration
The esophagus, stomach, large and small intestine, aided by the liver, gallbladder and pancreas convert the nutritive components of food into energy and break down the non-nutritive components into waste to be excreted.
Digestive system
illustration
-
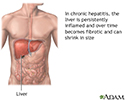
Aggressive hepatitis - illustration
Chronic active hepatitis is a liver disease caused by infection, drug ingestion, metabolic or autoimmune disorders. Necrosis (death) of liver cells, inflammation and fibrosis may lead to liver failure. Death within 5 years of onset occurs in 40% to 50% of patients.
Aggressive hepatitis
illustration
-
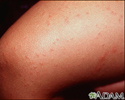
Gianotti-Crosti syndrome on the leg - illustration
Gianotti-Crosti disease is also called acrodermatitis of childhood. These red, elevated lesions do not contain pus and can occur on the limbs, buttocks, face, and neck.
Gianotti-Crosti syndrome on the leg
illustration
-
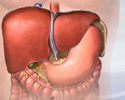
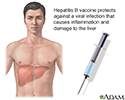
Hepatitis B - illustration
The hepatitis B vaccine is recommended for healthcare workers, people who live with someone with hepatitis B, and others at higher risk. The hepatitis B virus can damage liver cells. Immunization is also recommended for all infants and unvaccinated adolescents.
Hepatitis B
illustration
-
Hepatitis B virus - illustration
Hepatitis B is also known as serum hepatitis and is spread through blood and sexual contact. It is seen with increased frequency among intravenous drug users who share needles and among the homosexual population. This photograph is an electronmicroscopic image of hepatitis B virus particles. (Image courtesy of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.)
Hepatitis B virus
illustration
-
Digestive system - illustration
The esophagus, stomach, large and small intestine, aided by the liver, gallbladder and pancreas convert the nutritive components of food into energy and break down the non-nutritive components into waste to be excreted.
Digestive system
illustration
-
Aggressive hepatitis - illustration
Chronic active hepatitis is a liver disease caused by infection, drug ingestion, metabolic or autoimmune disorders. Necrosis (death) of liver cells, inflammation and fibrosis may lead to liver failure. Death within 5 years of onset occurs in 40% to 50% of patients.
Aggressive hepatitis
illustration
-
Gianotti-Crosti syndrome on the leg - illustration
Gianotti-Crosti disease is also called acrodermatitis of childhood. These red, elevated lesions do not contain pus and can occur on the limbs, buttocks, face, and neck.
Gianotti-Crosti syndrome on the leg
illustration
-
Hepatitis B - illustration
The hepatitis B vaccine is recommended for healthcare workers, people who live with someone with hepatitis B, and others at higher risk. The hepatitis B virus can damage liver cells. Immunization is also recommended for all infants and unvaccinated adolescents.
Hepatitis B
illustration
Review Date: 8/20/2015
Reviewed By: Subodh K. Lal, MD, gastroenterologist at Gastrointestinal Specialists of Georgia, Austell, GA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Internal review and update on 09/01/2016 by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.