Alcoholic neuropathy
Neuropathy - alcoholic; Alcoholic polyneuropathy
Alcoholic neuropathy is damage to the nerves that results from excessive drinking of alcohol.
Causes
The exact cause of alcoholic neuropathy is unknown. It likely includes both a direct poisoning of the nerve by the alcohol and the effect of poor nutrition associated with alcoholism. Up to half of long-term heavy alcohol users develop this condition.
In severe cases, nerves that regulate internal body functions (autonomic nerves) may be involved.
Risks of alcoholic neuropathy include:
- Long-term, heavy alcohol use
-
Alcoholism
that is present for 10 years or more
Alcoholism
Alcohol use disorder is when your drinking causes serious problems in your life, yet you keep drinking. You may also need more and more alcohol to f...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Symptoms
Symptoms of this condition include any of the following:
-
Numbness
in the arms and legs
Numbness
Numbness and tingling are abnormal sensations that can occur anywhere in your body, but they are often felt in your fingers, hands, feet, arms, or le...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Abnormal sensations
, such as "pins and needles"
Abnormal sensations
Numbness and tingling are abnormal sensations that can occur anywhere in your body, but they are often felt in your fingers, hands, feet, arms, or le...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Painful sensations in the arms and legs
-
Muscle problems, including
weakness
,
cramps
,
aches
, or spasms
Cramps
Muscle cramps are when a muscle gets tight (contracts) without you trying to tighten it, and it does not relax. Cramps may involve all or part of on...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleAches
Muscle aches and pains are common and can involve more than 1 muscle. Muscle pain also can involve ligaments, tendons, and fascia. Fascia are the s...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Heat intolerance
, especially after exercise
Heat intolerance
Heat intolerance is a feeling of being overheated when the temperature around you rises. It can often cause heavy sweating. Heat intolerance usually...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Erection problems (
impotence
)
Impotence
An erection problem occurs when a man cannot get or keep an erection that is firm enough for intercourse. You may not be able to get an erection at ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Problems urinating
,
incontinence
(leaking urine), feeling of incomplete bladder emptying,
difficulty beginning to urinate
Problems urinating
Difficulty starting or maintaining a urine stream is called urinary hesitancy.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleIncontinence
Urinary (or bladder) incontinence happens when you are not able to keep urine from leaking out of your urethra. The urethra is the tube that carries...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleDifficulty beginning to urinate
Difficulty starting or maintaining a urine stream is called urinary hesitancy.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Constipation or diarrhea
- Nausea, vomiting
- Problems swallowing or talking
Changes in muscle strength or sensation usually occur on both sides of the body and are more common in the legs than in the arms. Symptoms usually develop gradually and become worse over time.
Exams and Tests
The health care provider will perform a physical exam and ask about symptoms. An eye exam may show eye problems.
Alcoholism often makes the body unable to use or store certain vitamins and minerals. Blood tests will be ordered to check for a deficiency (lack) of:
-
Thiamine
(vitamin B1)
Thiamine
Thiamin is one of the B vitamins. The B vitamins are a group of water-soluble vitamins that are part of many of the chemical reactions in the body....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Pyridoxine
(vitamin B6)
Pyridoxine
Vitamin B6 is a water-soluble vitamin. Water-soluble vitamins dissolve in water so the body cannot store them. Leftover amounts of the vitamin leav...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Pantothenic acid and biotin
Pantothenic acid and biotin
Pantothenic acid and biotin are types of B vitamins. They are water-soluble, which means that the body can't store them. If the body can't use all ...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 is a water-soluble vitamin. Water-soluble vitamins dissolve in water. After the body uses these vitamins, leftover amounts leave the bo...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Folic acid
Folic acid
Folic acid is a type of B vitamin. It is the man-made (synthetic) form of folate that is found in supplements and added to fortified foods. Folate i...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Niacin
(vitamin B3)
Niacin
Niacin is a type of B vitamin. It is water-soluble, which means it is not stored in the body. Water-soluble vitamins dissolve in water. Leftover a...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Vitamin A
Vitamin A
Vitamin A is a fat-soluble vitamin that is stored in the liver. There are two types of vitamin A that are found in the diet. Preformed vitamin A is...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Other tests may be ordered to rule out other possible causes of neuropathy. Tests may include:
-
Electrolyte levels
Electrolyte levels
Electrolytes are minerals in your blood and other body fluids that carry an electric charge. Electrolytes affect how your body functions in many ways...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Electromyography (
EMG
)
EMG
Electromyography (EMG) is a test that checks the health of the muscles and the nerves that control the muscles.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Liver and kidney function tests
-
Thyroid function tests
Thyroid function tests
Thyroid function tests are used to tell whether your thyroid is working normally. The most common thyroid function tests are:Total, or free T4 (the m...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Levels of vitamins and minerals in the body
-
Nerve conduction tests
Nerve conduction tests
Nerve conduction velocity (NCV) is a test to see how fast electrical signals move through a nerve.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Nerve biopsy
Nerve biopsy
A nerve biopsy is the removal of a small piece of a nerve for examination.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Upper GI and small bowel series
Upper GI and small bowel series
An upper GI and small bowel series is a set of x-rays taken to examine the esophagus, stomach, and small intestine. Barium enema is a related test....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (
EGD
)
EGD
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) is a test to examine the lining of the esophagus, stomach, and first part of the small intestine.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Voiding cystourethrogram
Voiding cystourethrogram
A voiding cystourethrogram is an x-ray study of the bladder and urethra. It is done while the bladder is emptying.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
Once the alcohol problem has been addressed, treatment goals include:
- Controlling symptoms
- Maximizing ability to function independently
- Preventing injury
It is important to supplement the diet with vitamins, including thiamine and folic acid.
Physical therapy and orthopedic appliances (such as splints) may be needed to maintain muscle function and limb position.
Medicines may be needed to treat pain or uncomfortable sensations. People with alcoholic neuropathy have alcohol use problems. They will be prescribed the smallest dose of medicine needed to reduce symptoms, to help prevent drug dependence and other side effects of chronic use.
Chronic
Chronic refers to something that continues over an extended period of time. A chronic condition is usually long-lasting and does not easily or quick...

Positioning or the use of a bed frame that keeps the covers off the legs may help reduce pain.
People with lightheadedness or dizziness when standing up (orthostatic hypotension) may need to try several different treatments before finding one that successfully reduces their symptoms. Treatments that may help include:
-
Wearing
compression stockings
Compression stockings
Compression hose; Pressure stockings; Support stockings; Gradient stockings; Varicose veins - compression stockings; Venous insufficiency - compressi...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Eating extra salt
- Sleeping with the head elevated
- Using medicines
Bladder problems may be treated with:
- Manual expression of urine
-
Intermittent catheterization (
male
or
female
)
Female
Clean intermittent catheterization - female; CIC - female
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Medicines
Impotence, diarrhea, constipation, or other symptoms are treated when necessary. These symptoms often respond poorly to treatment in people with alcoholic neuropathy.
It is important to protect body parts with reduced sensation from injury. This may include:
- Checking the temperature of bath water to prevent burns
- Changing footwear
- Frequently inspecting the feet and shoes to reduce injury caused by pressure or objects in the shoes
- Guarding the extremities to prevent injury from pressure
Alcohol must be stopped to prevent the damage from getting worse. Treatment for alcoholism may include counseling, social support such as Alcoholics Anonymous (AA), or medicines.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Damage to nerves from alcoholic neuropathy is usually permanent. It is likely to get worse if the person continues to use alcohol or if nutritional problems are not corrected. Alcoholic neuropathy is usually not life-threatening, but it can severely affect quality of life.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call for an appointment with your health care provider if you have symptoms of alcoholic neuropathy.
Prevention
The only way to prevent alcoholic neuropathy is not to drink excessive amounts of alcohol.
References
Katri B, Koontz D. Disorders of the peripheral nerves. In: Daroff RB, Fenichel GM, Jankovic J, Mazziotta JC, eds. Bradley's Neurology in Clinical Practice . 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2012:chap 76.
Koppel BS. Nutritional and alcohol-related alcoholic disorders. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman's Cecil Medicine . 25th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2015:chap 416.
-
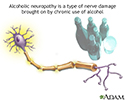
Alcoholic neuropathy - illustration
Alcoholic neuropathy is a disorder involving decreased nerve function due to the damage caused by habitual alcohol abuse. The damage may affect the autonomic nerves (those that regulate internal body functions) and the nerves that control movement and sensation.
Alcoholic neuropathy
illustration
-
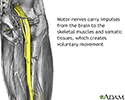
Motor nerves - illustration
Motor nerves are the nerves responsible for all voluntary skeletal and somatic movement such as moving the leg or arm.
Motor nerves
illustration
-
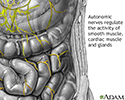
Autonomic Nerves - illustration
Autonomic nerves are concerned with muscular functions which are reflexive, such as breathing, heartbeats and peristalsis (rhythmic movements of the intestines).
Autonomic Nerves
illustration
-
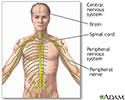
Central nervous system - illustration
The central nervous system is comprised of the brain and spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system includes all peripheral nerves.
Central nervous system
illustration
-
Alcoholic neuropathy - illustration
Alcoholic neuropathy is a disorder involving decreased nerve function due to the damage caused by habitual alcohol abuse. The damage may affect the autonomic nerves (those that regulate internal body functions) and the nerves that control movement and sensation.
Alcoholic neuropathy
illustration
-
Motor nerves - illustration
Motor nerves are the nerves responsible for all voluntary skeletal and somatic movement such as moving the leg or arm.
Motor nerves
illustration
-
Autonomic Nerves - illustration
Autonomic nerves are concerned with muscular functions which are reflexive, such as breathing, heartbeats and peristalsis (rhythmic movements of the intestines).
Autonomic Nerves
illustration
-
Central nervous system - illustration
The central nervous system is comprised of the brain and spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system includes all peripheral nerves.
Central nervous system
illustration
Review Date: 6/1/2015
Reviewed By: Daniel Kantor, MD, Kantor Neurology, Coconut Creek, FL and Immediate Past President of the Florida Society of Neurology (FSN). Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.