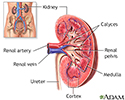
Renal scan
Renogram; Kidney scan
A renal scan is a nuclear medicine exam in which a small amount of radioactive material (radioisotope) is used to measure the function of the kidneys.
Nuclear medicine
A positron emission tomography scan is a type of imaging test. It uses a radioactive substance called a tracer to look for disease in the body. A po...

How the Test is Performed
The specific type of scan may vary. This article provides a general overview.
A renal scan is similar to a renal perfusion scintiscan . It may be done along with that test.
Renal perfusion scintiscan
A renal perfusion scintiscan is a nuclear medicine test. It uses a small amount of a radioactive substance to create an image of the kidneys....

You will be asked to lie on the scanner table. The health care provider will place a tight band or blood pressure cuff on your upper arm. This creates pressure and helps your arm veins become bigger. A small amount of radioisotope is injected into a vein. The specific radioisotope used may vary, depending on what is being studied.
Radioisotope
A positron emission tomography scan is a type of imaging test. It uses a radioactive substance called a tracer to look for disease in the body. A po...

The cuff or band on the upper arm is removed, and the radioactive material moves through your blood. The kidneys are scanned a short time later. Several images are taken, each lasting 1 or 2 seconds. The total scan time takes about 30 minutes to 1 hour.
A computer reviews the images and provides detailed information about how your kidney works. For example, it can tell your doctor how much blood the kidney filters over time. A diuretic drug ("water pill") may also be injected during the test. This helps speed up the passage of radioisotope through your kidneys.
You should be able to go home after the scan. You may be asked to drink plenty of fluids and urinate often to help remove the radioactive material from the body.
How to Prepare for the Test
Tell your health care provider if you take any nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or blood pressure medicines. These drugs might affect the test.
You may be asked to drink additional fluids before the scan.
How the Test will Feel
Some people feel discomfort when the needle is placed into the vein. However, you will not feel the radioactive material. The scanning table may be hard and cold. You will need to lie still during the scan. You may feel an increased urge to urinate near the end of the test.
Why the Test is Performed
A renal scan tells your provider how your kidneys work. It also shows their size, position, and shape. It may be done if:
- You cannot have other x-rays using contrast (dye) material because you are sensitive or allergic to them, or you have reduced kidney function
- You have had a kidney transplant and your doctor wants to check how well the kidney is working and look for signs of rejection
- You have high blood pressure and your doctor wants to see how well your kidneys are working
What Abnormal Results Mean
Abnormal results are a sign of reduced kidney function. This may be due to:
- Acute or chronic kidney failure
- Chronic kidney infection (pyelonephritis)
- Complications of a kidney transplant
-
Glomerulonephritis
Glomerulonephritis
Glomerulonephritis is a type of kidney disease in which the part of your kidneys that helps filter waste and fluids from the blood is damaged....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Hydronephrosis
-
Injury of the kidney and ureter
Injury of the kidney and ureter
Injury to the kidney and ureter is damage to the organs of the upper urinary tract.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Narrowing or blockage of the arteries that carry blood to the kidney
- Obstructive uropathy
Risks
There is a slight amount of radiation from the radioisotope. Most of this radiation exposure occurs to the kidneys and bladder. Almost all radiation is gone from the body in 24 hours. Caution is advised if you are pregnant or breastfeeding.
Very rarely, a person will have an allergic reaction to the radioisotope, which may include severe anaphylaxis .
Allergic reaction
Allergic reactions are sensitivities to substances called allergens that come into contact with the skin, nose, eyes, respiratory tract, and gastroin...

Anaphylaxis
Anaphylaxis is a life-threatening type of allergic reaction.

References
Fulgham PF, Bishoff JT. Urinary tract imaging: Basic principles. In: Wein AJ, ed. Campbell-Walsh Urology . 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2011:chap 4.
-
Kidney anatomy - illustration
The kidneys are responsible for removing wastes from the body, regulating electrolyte balance and blood pressure, and stimulating red blood cell production.
Kidney anatomy
illustration
-
Kidney - blood and urine flow - illustration
This is the typical appearance of the blood vessels (vasculature) and urine flow pattern in the kidney. The blood vessels are shown in red and the urine flow pattern in yellow.
Kidney - blood and urine flow
illustration
-
Kidney anatomy - illustration
The kidneys are responsible for removing wastes from the body, regulating electrolyte balance and blood pressure, and stimulating red blood cell production.
Kidney anatomy
illustration
-
Kidney - blood and urine flow - illustration
This is the typical appearance of the blood vessels (vasculature) and urine flow pattern in the kidney. The blood vessels are shown in red and the urine flow pattern in yellow.
Kidney - blood and urine flow
illustration
Review Date: 1/21/2015
Reviewed By: Scott Miller, MD, urologist in private practice in Atlanta, GA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.