Acne - self-care
Acne vulgaris - self-care; Cystic acne - self-care; Pimples - self-care; Zits - self-care
Acne is a skin condition that causes pimples or "zits." Whiteheads (closed comedomes), blackheads (open comdedomes), and red, inflamed papules of skin (such as cysts) may develop. These most often occur on the face or shoulders.
Acne occurs when tiny holes on the surface of the skin become clogged. These holes are called pores. The pores can become clogged by substances on the surface of the skin or when the skin itself produces "plugs." Acne is most common in teenagers. But anyone can get acne.
Acne breakouts can be triggered by:
- Hormonal changes
- Use of oily skin or hair care products
- Certain medicines
- Sweat
- Humidity
- Diet
Daily Skin Care
To keep your pores from clogging and your skin from becoming too oily:
- Clean your skin gently with a mild, non-drying soap, such as Dove, Neutrogena, Cetaphil, or CeraVe.
- It may help to use a wash with salicylic acid or benzoyl if your skin is oily and prone to acne. Remove all dirt or make-up.
- Wash once or twice a day, and also after exercising. Avoid scrubbing or repeated skin washing.
- Shampoo your hair daily, especially if it is oily.
- Comb or pull your hair back to keep the hair out of your face.
- Avoid using rubbing alcohol or toners that are very drying to the skin.
Acne medicines can cause skin drying or peeling. Use a moisturizer or skin cream that is water-based or "noncomedogenic" or that clearly states that is safe to use on the face and will not cause acne.
A small amount of sun exposure may improve acne slightly. But tanning mostly hides it. Too much exposure to sun or in tanning booths increases the risk for skin cancer. Some acne medicines can make your skin more sensitive to the sun. Use sunscreen and hats regularly if you are taking these medicines.
There is no evidence that you need to avoid chocolate, milk, or high-fat foods. High sugar intake may need to worsening acne. Avoid any of these foods if you find eating these foods seems to make your acne worse.
To further prevent acne:
- DO NOT squeeze, scratch, pick, or rub pimples. This can lead to skin infections and scarring.
- Avoid wearing tight headbands, baseball caps, and other hats.
- Avoid touching your face.
- Avoid greasy cosmetics or creams.
- DO NOT leave make-up on overnight.
Acne Medicines
If daily skin care does not clear up blemishes, try over-the-counter acne medicines that you apply to your skin.
- These products may contain benzoyl peroxide, sulfur, resorcinol, or salicylic acid.
- They work by killing bacteria, drying up skin oils, or causing the top layer of your skin to peel.
- They may cause redness or peeling of the skin.
Treatments From Your Health Care Provider
If pimples are still a problem after you've tried over-the-counter medicines, your health care provider may suggest:
- Antibiotics in the form of pills or creams that you put on your skin
- Prescription gels or creams containing a retinoid to help clear up the pimples
- Hormone pills for women whose acne is made worse by hormonal changes
- Isotretinoin pills for severe acne
- A laser procedure called photodynamic therapy
- Chemical skin peeling
When to Call the Doctor
Call your health care provider or a dermatologist if:
- Self-care steps and over-the-counter medicine do not help after several months.
- Your acne is very bad (for example, you have a lot of redness around the pimples, or you have cysts).
- Your acne is getting worse.
- You develop scars as your acne clears up.
- Acne is causing emotional stress.
References
James WD, Berger TG, Elston DM. Acne. In: James WD, Berger TG, Elston DM, eds. Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology . 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2016:chap 13
Zaenglein AL, Thiboutot DM. Acne vulgaris. In: Bolognia JL, Jorizzo JL, Schaffer JV, et al, eds. Dermatology . 3rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Mosby; 2012:chap 36.
-
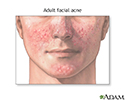
Adult facial acne - illustration
Acne may persist into adulthood.
Adult facial acne
illustration
-
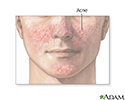
Acne - illustration
Acne is inflammation of the sebaceous glands in the skin. When the pores of the skin become clogged, the oil the sebaceous gland secretes becomes trapped. The plug causes the follicle to bulge (causing whiteheads), and the top of the plug may darken (causing blackheads).
Acne
illustration
-
Adult facial acne - illustration
Acne may persist into adulthood.
Adult facial acne
illustration
-
Acne - illustration
Acne is inflammation of the sebaceous glands in the skin. When the pores of the skin become clogged, the oil the sebaceous gland secretes becomes trapped. The plug causes the follicle to bulge (causing whiteheads), and the top of the plug may darken (causing blackheads).
Acne
illustration
Review Date: 1/31/2016
Reviewed By: Kevin Berman, MD, PhD, Atlanta Center for Dermatologic Disease, Atlanta, GA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.