Upper airway biopsy
Biopsy - upper airway
Upper airway biopsy is surgery to remove a small piece of tissue from the nose, mouth, and throat area for examination.
How the Test is Performed
The health care provider will spray a numbing medicine in your mouth and throat. A metal tube is inserted to hold your tongue out of the way.
Another numbing medicine flows through the tube down the back of the throat. This may cause you to cough at first. When the area feels thick or swollen, it is numb.
The are provider looks at the abnormal area, and removes a small piece of tissue. It is sent to the laboratory for examination.
How to Prepare for the Test
DO NOT eat for 6 to 12 hours before the test.
Tell your provider if you take a blood thinner, such as aspirin, plavix or coumadin, when you schedule the biopsy. You may need to stop taking them for a little while. Never stop taking any medicines without first talking to your provider.
How the Test will Feel
As the area is being numbed, you may feel like there is fluid running down the back of your throat. You may feel the need to cough or gag. And you may feel pressure or mild tugging.
When the numbness wears off, your throat may feel scratchy for several days. After the test, the cough reflex will return in 1 to 2 hours. Then you may eat and drink normally.
Why the Test is Performed
This test may be done if your doctor thinks there is a problem with your upper airway. It may also be done with a bronchoscopy .
Bronchoscopy
Bronchoscopy is a test to view the airways and diagnose lung disease. It may also be used during the treatment of some lung conditions.

Normal Results
The upper airway tissues are normal, with no abnormal growths.
What Abnormal Results Mean
Disorders or conditions that may be discovered include:
- Benign (noncancerous) cysts or masses
-
Cancer
Cancer
Cancer is the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells in the body. Cancerous cells are also called malignant cells.
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Certain infections
-
Granulomas
and related inflammation (may be caused by
tuberculosis
)
Granulomas
Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA) is a rare disorder in which blood vessels become inflamed. This leads to damage in major organs of the body. ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleTuberculosis
Pulmonary tuberculosis (TB) is a contagious bacterial infection that involves the lungs. It may spread to other organs.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Autoimmune disorders, such as Wegner's granulomatosis
-
Necrotizing vasculitis
Necrotizing vasculitis
Necrotizing vasculitis is a group of disorders that involve inflammation of the blood vessel walls. The size of the affected blood vessels helps to ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Risks
Risks for this procedure include:
- Bleeding (some bleeding is common, heavy bleeding is not)
- Breathing difficulties
- Sore throat
There is a risk of choking if you swallow water or food before the numbness wears off.
References
Yung RC, Boss EF. Tracheobronchial endoscopy. In: Flint PW, Haughey BH, Lund LJ, et al, eds. Cummings Otolaryngology: Head & Neck Surgery. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Mosby; 2010:chap 75.
-
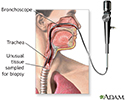
Upper airway test - illustration
An upper airway biopsy is obtained by using a flexible scope called a bronchoscope. The scope is passed down through the mouth and throat and a small piece of tissue is removed and sent to the laboratory. This test may be performed when an abnormality of the upper airway is suspected. It may also be performed as part of a bronchoscopy when abnormalities include the upper airway as well as the lung tissue.
Upper airway test
illustration
-
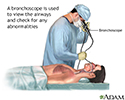
Bronchoscopy - illustration
Bronchoscopy is a surgical technique for viewing the interior of the airways. Using sophisticated flexible fiber optic instruments, surgeons are able to explore the trachea, main stem bronchi, and some of the small bronchi. In children, this procedure may be used to remove foreign objects that have been inhaled. In adults, the procedure is most often used to take samples of (biopsy) suspicious lesions and for culturing specific areas in the lung.
Bronchoscopy
illustration
-
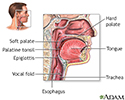
Throat anatomy - illustration
Structures of the throat include the esophagus, trachea, epiglottis and tonsils.
Throat anatomy
illustration
-
Upper airway test - illustration
An upper airway biopsy is obtained by using a flexible scope called a bronchoscope. The scope is passed down through the mouth and throat and a small piece of tissue is removed and sent to the laboratory. This test may be performed when an abnormality of the upper airway is suspected. It may also be performed as part of a bronchoscopy when abnormalities include the upper airway as well as the lung tissue.
Upper airway test
illustration
-
Bronchoscopy - illustration
Bronchoscopy is a surgical technique for viewing the interior of the airways. Using sophisticated flexible fiber optic instruments, surgeons are able to explore the trachea, main stem bronchi, and some of the small bronchi. In children, this procedure may be used to remove foreign objects that have been inhaled. In adults, the procedure is most often used to take samples of (biopsy) suspicious lesions and for culturing specific areas in the lung.
Bronchoscopy
illustration
-
Throat anatomy - illustration
Structures of the throat include the esophagus, trachea, epiglottis and tonsils.
Throat anatomy
illustration
Review Date: 11/25/2014
Reviewed By: Ashutosh Kacker, MD, BS, Professor of Clinical Otolaryngology, Weill Cornell Medical College, and Attending Otolaryngologist, New York-Presbyterian Hospital, New York, NY. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.