Tympanometry
Tympanogram; Otitis media - tympanometry; Effusion - tympanometry
Tympanometry is a test used to detect problems in the middle ear.
How the Test is Performed
Before the test, your health care provider will look inside your ear to make sure nothing is blocking the eardrum.
Next, a device is placed into your ear. This device changes the air pressure in your ear and makes the eardrum move back and forth. A machine records the results on graphs called tympanograms.
How to Prepare for the Test
You should not move, speak, or swallow during the test. Such movements can change the pressure in the middle ear and give incorrect test results.
The sounds heard during the test may be loud. This may be startling. You will need to try very hard to stay calm and not get startled during the test. If your child is to have this test done, it may be helpful to show how the test is done using a doll. The more your child knows what to expect and why the test is done, the less nervous your child will be.
How the Test will Feel
There may be some discomfort while the probe is in the ear, but no harm will result. You will hear a loud tone and feel pressure in your ear as the measurements are taken.
Why the Test is Performed
This test measures how your ear reacts to sound and different pressures.
Normal Results
The pressure inside the middle ear can vary by a very small amount. The eardrum should look smooth.
What Abnormal Results Mean
Tympanometry may reveal any of the following:
-
A
tumor
in the middle ear
Tumor
A tumor is an abnormal growth of body tissue. Tumors can be cancerous (malignant) or noncancerous (benign).
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Fluid in the middle ear
-
Impacted
ear wax
Ear wax
The ear canal is lined with hair follicles. The ear canal also has glands that produce a waxy oil called cerumen. The wax will most often make its ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Lack of contact between the conduction bones of the middle ear
- Perforated eardrum
- Scarring of the tympanic membrane
Risks
There are no risks with this test.
References
Amundsen GA. Tympanometry. In: Pfenninger JL, Fowler GC, eds. Pfenninger and Fowler's Procedures for Primary Care . 3rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Mosby; 2011:chap 75.
Bauer CA, Jenkins HA. Otologic symptoms and syndromes. In: Flint PW, Haughey BH, Lund V, et al, eds. Cummings Otolaryngology: Head & Neck Surgery . 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2015:chap 156.
Lieberthal AS, Carroll AE, Chonmaitree T, et al. The diagnosis and management of acute otitis media. Pediatrics . 2013;131(3):e964-e999. PMID: 23439909. www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23439909 .
-
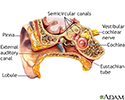
Ear anatomy - illustration
The ear consists of external, middle, and inner structures. The eardrum and the 3 tiny bones conduct sound from the eardrum to the cochlea.
Ear anatomy
illustration
-
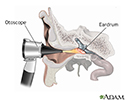
Otoscope examination - illustration
An otoscope is a tool which shines a beam of light to help visualize and examine the condition of the ear canal and eardrum. Examining the ear can reveal the cause of symptoms such as an earache, the ear feeling full, or hearing loss.
Otoscope examination
illustration
-
Ear anatomy - illustration
The ear consists of external, middle, and inner structures. The eardrum and the 3 tiny bones conduct sound from the eardrum to the cochlea.
Ear anatomy
illustration
-
Otoscope examination - illustration
An otoscope is a tool which shines a beam of light to help visualize and examine the condition of the ear canal and eardrum. Examining the ear can reveal the cause of symptoms such as an earache, the ear feeling full, or hearing loss.
Otoscope examination
illustration
Review Date: 5/18/2016
Reviewed By: Neil K. Kaneshiro, MD, MHA, Clinical Assistant Professor of Pediatrics, University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.